Vision
 Visual system consist of the eyes, the accessory structures, and the sensory neurons that project to the cerebral cortex where action potential conveying visual information are interpreted.
Visual system consist of the eyes, the accessory structures, and the sensory neurons that project to the cerebral cortex where action potential conveying visual information are interpreted.
EYEBROWS
Curved lines of hair over the orbit. Protect the eyes by preventing perspiration from running down the forehead, entering the eyes and cause irritation.
EYELIDS
Movable folds covering the anterior surface of the eye when closed. Contain caruncle that contains modified sebaceous and sweat gland. They protect the eyes from foreign objects by blinking action, which also will lubricate the eyes by spreading tears over the surface. Eyelids also help to regulate the amount of light entering the eye. Eyelashes are attached as a double or triple row of hairs to the free edges of eyelids.
CONJUNCTIVA
A thin, transparent mucous membrane. It covers the inner surface of the eyelids and the anterior white surface of the eye. It acts as barrier against microorganisms and to reduce friction due to movement of eyelids.
LACRIMAL APPARATUS
Consist of lacrimal gland, lacrimal canaliculi, and nasolacrimal duct.
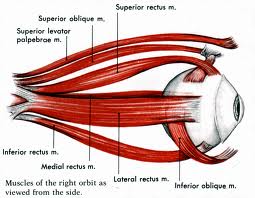
EXTRINSIC EYE MUSCLES
These muscles attach to the outside of the eyeball and cause it to move. There are four rectus (straight) muscles, the superior, inferior, medial and lateral rectus muscles. There are two oblique muscles, the superior and inferior oblique muscles.
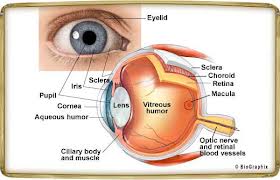
LAYER OF EYES
Sclera: firm, opaque, white, outer layer of the eyeball. It consist of dense collagenous connective tissue with elastic fibers. It helps in maintain the shape of the eyeball, protects its internal structures, and provides an attachment point for the extrinsic eye muscles.
Cornea: avascular and transparent, permitting light to enter the eye. Responsible for most of the refraction of the light entering the eye. It consists of connective tissue matrix containing collagen, elastic fibers and proteoglycans, with a layer of stratified squamous epithelium covering the outer surface and a layer of simple squamous epithelium on the inner surface.
VASCULAR LAYER
Choroid: very thin structure consisting a vascular network and many melanin-containing pigment cells so that it appears black in color. The black color absorb light so that it is not reflected inside the eye and interrupt the vision.
Ciliary Body: consist of ciliary ring and ciliary processes that contain smooth muscles that will control the changing in the eye’s shape.
Iris: the “colored part” of the eye. It is a contractile structure, mainly consist of smooth muscles .
Pupil: surrounded by smooth muscle. Light enter the eye through the pupil, and the iris regulate the amount of the light by controlling the size of the pupil.
RETINA
Retina is the inner surface of the eye, covering the inner surface of the eye posterior to the ciliary body. It has over 126 million photoreceptor cells which respond to light. Near the center of the posterior retina is a small yellow spot (4 mm diameter) the macula that contain the fovea centralis.
LENS
An avascular, transparent, biconcave disk located behind the pupil. The lens is part of the focusing system of the eye, and light passing through the lens is focused on the retina. The lens is a flexible structure, and changing the shape of the lens is involved with adjusting the focus of the light. It consists of a layer of cuboidal epithelial cells on its anterior surface and a posterior surface of a very long, columnar epithelial cells called lens fibers.